Title:
Techniques for Image Steganography
Objective:
To research and understand the techniques used in Image Steganography
Content/Result:
To hide a message inside an image without changing its visible properties, the cover source can be altered in ”noisy”areas with many color variations, so less attention will be drawn to the modifications. The most common methods to make these alterations involve the usage of the least-significant bit (LSB), masking, filtering and transformations on the cover image. These techniques can be used with varying degrees of success on different types of image files.
The simplest steganography techniques embed the bits of the message directly into least significant bit plane of the cover image in a deterministic sequence. Modulating the least significant bit does not result in human-perceptible difference because the amplitude of the change is small
b) Masking and Filtering
Masking and filtering techniques, usually restricted to 24 bits or grayscale images, take a different approach to hiding a message. These methods are effectively similar to paper watermarks, creating markings in an image. This can be achieved for example by modifying the luminance of parts of the image.
c) Transformation
A more complex way of hiding a secret inside an image comes with the use and modifications of discrete cosine transformations. Discrete cosine transformations (DST)), are used by the JPEG compression algorithm to transform successive 8 x 8 pixel blocks of the image, into 64 DCT coefficients each. Each DCT coefficient F(u, v) of an 8 x 8 block of image pixels f(x, y) is given by:
Conclusion:
The most common techniques used in Image Steganography is Least Significant Bit (LSB), Masking and Filtering, and also Transformation.

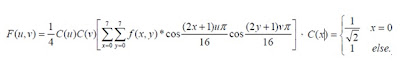

No comments:
Post a Comment