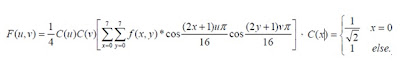Title:
MATLAB Basic Class
Objective:
To explore about MATLAB Basic Features
Content/Result:
This week I explored about MATLAB features and function. I refer to this link: http://www.mathworks.com/help/ as well as some notes given by Madam Lily. Below are some of the examples of my learning.
1) To display text
a=input('Have a nice day!');
disp(a)
b=input('GOOD LUCK IN YOUR EXAM');
disp(b)
c=input('Hello everyone');
disp(c)
disp(a)
b=input('GOOD LUCK IN YOUR EXAM');
disp(b)
c=input('Hello everyone');
disp(c)
2)Vector
A = [ [1 2 3]' [3 2 1]' [2 1 3]'];B = A;
for j=2:3,
A(j,:) = A(j,:) - A(j-1,:)
end
Output: A = 1 3 2
1 -1 -1
3 1 3
A = 1 3 2
1 -1 -1
2 2 4
3) The Colon Notation
1:4
ans =
1 2 3 4
3:7
ans =
3 4 5 6 7
Conclusion: